Parenteral Nutrition Definition Veterinary
Nutrition by intravenous feeding may be either total parenteral nutrition or only supplemental. A veterinary facility with the ability to obtain and maintain aseptic vascular access to provide attentive 24-hour nursing care and to perform in-house serum chemistry analysis can provide parenteral nutritional support.

Parenteral Nutrition Uses Indications And Compounding Vetfolio
Parenteral nutrition is the practice of feeding into the bloodstream ie.

Parenteral nutrition definition veterinary. The medical records of all dogs and cats receiving PPN between 1994 and 1999 were reviewed to determine signalment reasons for use of PPN duration of PPN administration duration of hospitalization complications and mortality. Administration through routes other than the gastrointestinal tract. Certain key nutritional factors play a role in managing vomiting and diarrhea in cats and dogsthrough enteral and parenteral nutritionand veterinary nurses should recognize the circumstances and reasoning for the key nutritional factors to ensure a positive outcome for patients with pancreatitis.
The average daily cost of total parenteral nutrition TPN hereafter referred to as central parenteral nutrition CPN for maintaining the caloric requirements of a. Parenteral nutrition can be delivered through a central vein central PN or CPN or a peripheral vein partial PN or PPN. The rationale for prescribing enteral nutrition rather than parenteral nutrition PN is based on the superior maintenance of intestinal structure and function 2 reduced infection rates 3 and reduced cost of enteral alimentation.
CPN is the provision of all of the animals calorie and protein requirements. For the term parenteral may also exist other definitions and meanings the meaning and definition indicated above are indicative not be used for medical and legal or special purposes. Parenteral nutrition should be used only when enteral feeding is not possible.
See Parenteral fluids comparison table. Allenspach K Gaschein FP. Meaning and definition of parenteral.
See Other Nutrient Requirements section. Parenteral nutrition includes solutions that provide protein carbohydrate and fat. TPN as defined in this chapter is the provision of all of the animals calorie and protein requirements and ideally all of the micronutrient requirements as well.
Conclusion Nutritional support in the critically ill patient is aimed at enhancing the rate of recovery and minimizing the impact of malnutrition. Parenteral nutrition a technique for meeting a patients nutritional needs by means of intravenous feedings. Parenteral nutrition PN is a nutritionally balanced solution that provides calories and nutrients to patients that cannot tolerate enteral nutrition or should not be fed by mouth.
Veterinary terminology Glossary of veterinary terms. Parenteral nutrition is feeding a person intravenously bypassing the usual process of eating and digestion. Parenteral nutrition is complicated and more expensive compared with enteral nutrition.
PN provides caloric protein and micronutrient requirements and should be administered only via a central venous catheter because of its high osmolality. Partial parenteral nutrition supplies only part of daily nutritional requirements supplementing oral intake. Parenteral nutrition is an important method of nutritional support in hospitalized animals but minimal information has been published on its use in camelids.
Parenteral nutrition is by definition given IV. Total parenteral nutrition TPN. By definition parenteral nutrition is any nutrition provided through an intravenous route that is composed of one or more of the three foundations of nutrition.
Many hospitalized patients are given dextrose or amino acid solutions by this method. The purpose of this retrospective study was to evaluate the use of partial parenteral nutrition PPN in dogs and cats. Total Parenteral or Partial Parenteral Nutrition When animals are critically ill or cannot take in enough calories intravenous nutrition may be required.
The person receives nutritional formulae that contain nutrients such as glucose amino acids lipids and added vitamins and dietary minerals. Fat intravenous lipid protein amino acids and carbohydrate dextrose. Parenteral nutrition involves the administration of essential nutrients by intravenous infusion.
Parenteral nutrition may be indicated for patients at significant risk for complications with enteral feeding. PPN only supplies part of the animals energy and nutrient requirements Chan. Sometimes called hyperalimentation even though it does not provide excessive amounts of nutrients.
Delaney et al 2006. Parenteral nutrition can be delivered via a central vein TPN or a peripheral vein PPN. When patients are unable to tolerate enteral feeding parenteral intravenous nutrition should be considered.
Adequate and proper nutrition is very important for pets that are hospitalized and has a great impact on.

Parenteral Nutrition Uses Indications And Compounding Vetfolio
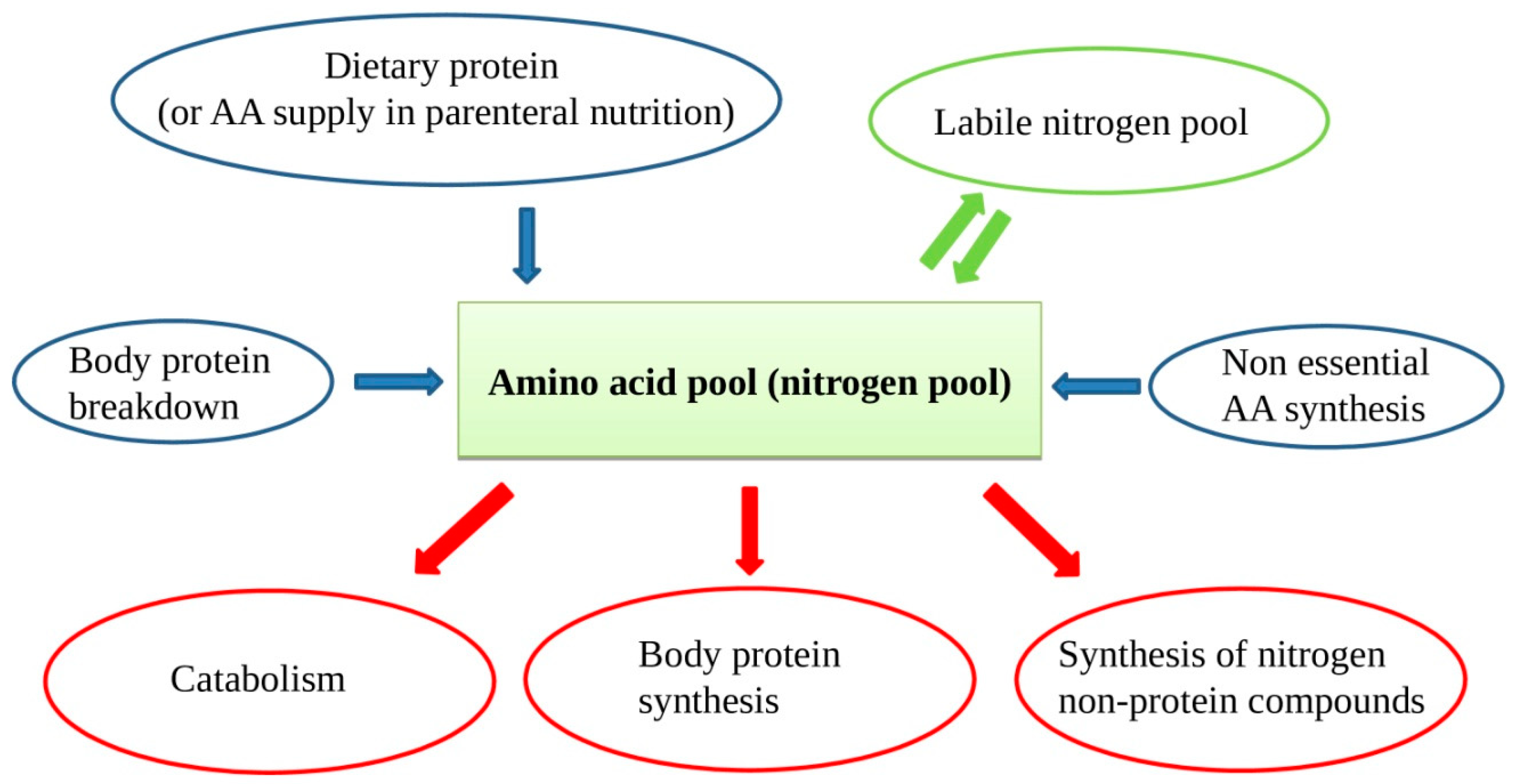
Nutrients Free Full Text Macronutrients In Parenteral Nutrition Amino Acids Html

Parenteral Nutrition Uses Indications And Compounding Vetfolio

Parenteral Nutrition Uses Indications And Compounding Vetfolio

Enteral Vs Parenteral Nutrition Study Com

Parenteral Nutrition Formulation Monitoring And Complications Vetfolio
Section 1 Types Of Nutrition Support

Pin By Nicolette Geiger On Pathophysiology Nursing Notes Dysphagia Therapy Nursing Mnemonics

Post a Comment for "Parenteral Nutrition Definition Veterinary"